Detrimental effects may last 72 h or more after. Click again to see term.
Placenta accreta has become an important cause of maternal morbidity and mortality.

. Clinicians Brief July 2016. For example more than half of women are transfused or admitted to an intensive care unit. Meperidine is commonly used during labour.
Amnionic sac chorionic sac yolk sac and allantois. The word -- is Latin for poison and refers to a particular group of pathogens. Tap again to see term.
Found in mucous saliva tears and breast milk. However animal and organ culture models agree that most placental infections originate in the uterine decidua 2 which is minimally accessible from the maternal blood. The _____ _____ _____are the only areas of the GI tract that harbor permanent resident microbes.
Maternal infections caused by most organisms which can cross the placenta including. Viruses are not visualized by light microscopes. HIV Toxoplasma gondii Varicella-zoster virus Staphylococcus aureus HIV HSV 1 and 2 Hepatitis B virus and Toxoplasma gondii Neisseria gonorrhoeae Toxoplasma gondii HIV Hepatitis B virus.
Which of the following terms is used to describe the inside chamber of a structure eg inside the small intestine or inside the endoplasmic reticulum. Part of the B cell receptor. This work is published on September 17 on Natures website.
All opioids cross the placenta in significant amounts. Just for example it has great lipid solubility low molecular weight 3659 daltons and a measured in vitro plasma protein binding of 70 to 76. Pregnant women are thus advised to avoid consumption of soft.
Protects against parasitic worms. Some of the most common pathogens that are able to cross and infect the placental barrier are referred to as torch toxoplasma gondii others including varicella zoster virus parvovirus b19. While some pathogens have developed mechanisms to cross the placenta and directly infect the fetus other pathogens lead to an upregulation in maternal or placental inflammation that can indirectly cause harm.
It has been postulated that the unique immunological environment in the placentanecessary to assure tolerance of the fetal. The reason for the predisposition of placental infection toward intracellular pathogens is unclear. This page will not cover the whole placenta just the development of the extra-embryonic membranes that form the extra-embryonic coeloms cavities or spaces.
Protozoan bacteria DNA and RNA viruses. Transplacental transmission also allows vector-borne diseases to cycle when vectors are not active or present in a geographic area and can contribute to introduction and establishment of parasites where they previously did not occur. The placental membranes is a term often used to describe the all the fetal components of the placenta Greek plakuos flat cake.
Listeria infection is relatively common among pregnant women because the elevated levels of progesterone downregulate the immune system making them more vulnerable to infection. Damage of the syncytiotrophoblast enables pathogens green stars that are free in maternal blood or inside of maternal leukocytes yellow cells with green stars to cross into fetal tissues 1. It is striking that the majority of pathogens that are able to cross the placenta have either facultative or obligate intracellular life cycles.
Drugs such as alcohol and nicotine can cross the placenta. Cord blood - human umbilical cord blood HUCB A term used to describe blood collected from the placenta usually after birth. Some of the most common pathogens that are able to cross and infect the placental barrier are referred to as TORCH Toxoplasma gondii others including varicella zoster virus parvovirus B19 human immunodeficiency virus HIV enteroviruses Listeria monocytogenes and Treponema pallidum causing syphilis rubella cytomegalovirus CMV and herpes simplex.
Maximal uptake by the fetal tissues occurs 23 h after a maternal im. This is the first time the molecular mechanism allowing a pathogenic bacterium to cross the placenta in vivo is discovered. All of the other sections of.
You will see that antibodies are small enough to cross the placenta. The techniques used to observe other pathogens were useless with viruses. Widespread in nature water soil plants animals that.
Routes used by TORCH pathogens to overcome the placental barrier. This is why it is so vital that pregnant mothers do not smoke and drink to ensure that the foetus development is not affected by. Dose and this is the time when neonatal respiratory depression is most likely to occur.
A very small number of viruses including rubella virus Zika virus and cytomegalovirus CMV can travel across the placental barrier generally taking advantage of conditions at certain gestational periods as the placenta develops. This occurs in about 1 prevents the passage. The pathogen can cross the placenta and infect the fetus often resulting in miscarriage stillbirth or fatal neonatal infection.
Tap card to see definition. Zofran ondansetron has properties that cause it to easily cross the placenta in substantial amounts. Cord knotting Term describing umbilical or placental cord knotting.
Which of the following which are considered coliforms. Terms in this set 19 types of pathogens. Escherichia coli Citrobacter Enterobacter.
Press release Paris september 17 2008 Listeriosis is a bacterial infection caused by food-borne Listeria monocytogenes. Masses pale infarcts lace-like bands etc. It is 50 plasma protein-bound and crosses the placenta readily.
Its not an immune system per se but the placenta contains a whole network of macrophages white blood cells that engulf viruses and other pathogens. Has been identified as a source of stem cells with potential therapeutic uses and is stored in Cord Blood Banks throughout the world. The placenta is a temporary yet critical organ that serves multiple important functions during gestation including facilitation of fetal nutrition.
Toxoplasma gondii adult condition. There are several pathways by which Zika virus ZIKV and other TORCH. Missing cotyledons or extremely fragmented parenchyma which may be indications of retained placenta should be noted Serially section the disc at 1 to 2 cm intervals and examine each slice for intraparenchymal lesions eg.
Secreted by plasma cells in. Also tissues are continually formed and broken down as the placenta grows and builds the umbilical cord. QUESTION 7 Pathogens able to cross the placental barrier include.
Responsible for allergic reactions. The macrophages migrate throughout the maternal side of the placenta to clear dead cells. Some of the most common pathogens that are able to cross and infect the placental barrier are referred to as TORCH T oxoplasma gondii others including varicella zoster virus parvovirus B19 human immunodeficiency virus HIV enteroviruses Listeria monocytogenes and Treponema pallidum causing syphilis rubella cytomegalovirus CMV and herpes simplex.
Neospora caninum Babesiosis Leishmaniasis Dirofilarial microfilariae Source. Article the term placenta accreta is used as a general term to describe all of these three conditions whereas the term percreta refers to placenta percreta 2. Activates basophils and mast cells.
Click card to see definition. This gives the baby a passive immunity that can protect it for a short time from any pathogens it encounters. CMV and Zika travel from the maternal bloodstream via placental cells to the fetal bloodstream.
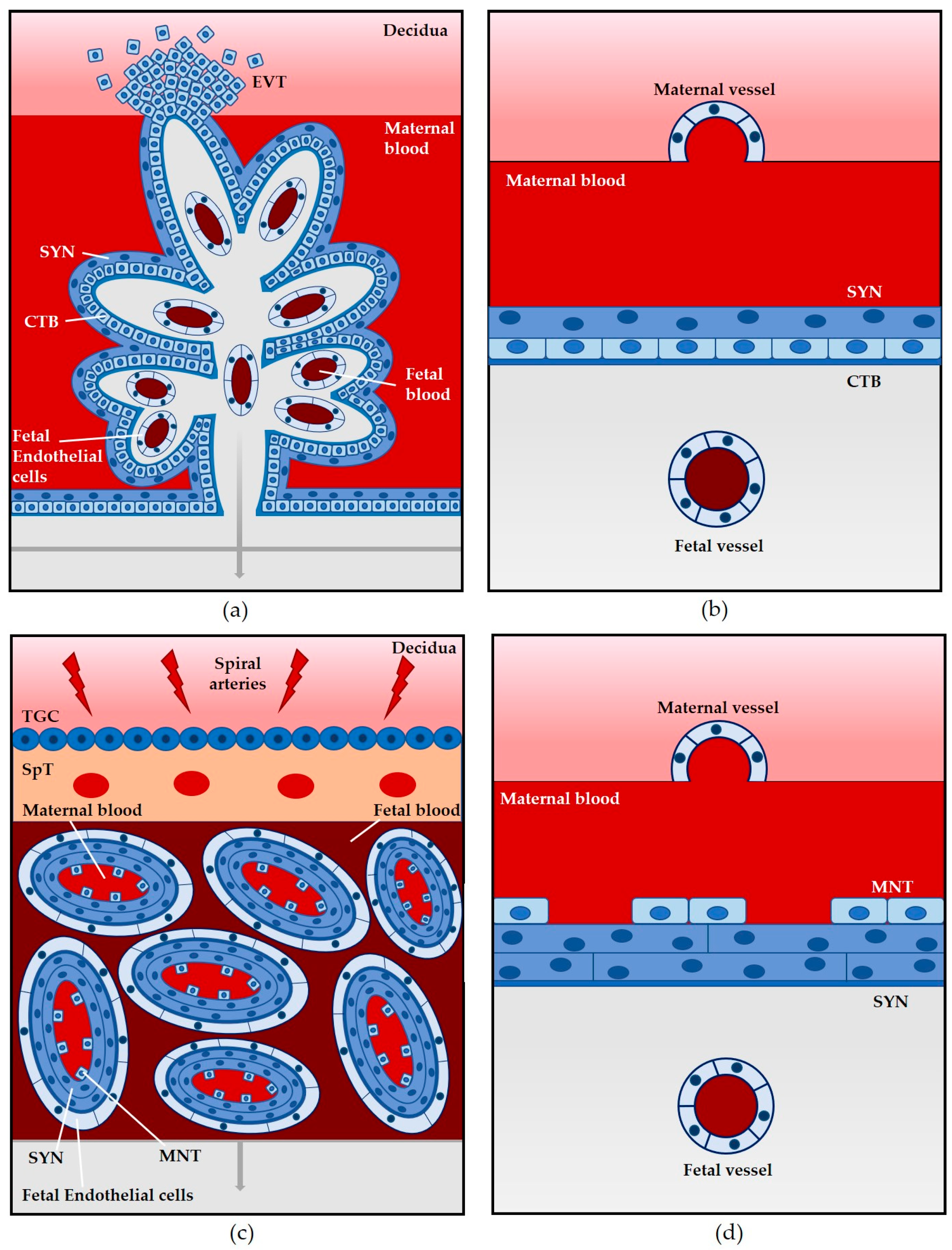
Pathogens Free Full Text Vertical Transmission Of Listeria Monocytogenes Probing The Balance Between Protection From Pathogens And Fetal Tolerance Html


0 Comments